
The Knoevenagel reaction is a carbonyl condensation reaction of an ester with an aldehyde or ketone to yield an \alpha , \beta -unsaturated product. Show the mechanism for the Knoevenagel reaction

The plausible mechanism of the Knoevenagel condensation in the medium... | Download Scientific Diagram

Scheme 2. Possible mechanism of the Knoevenagel condensation in the... | Download Scientific Diagram
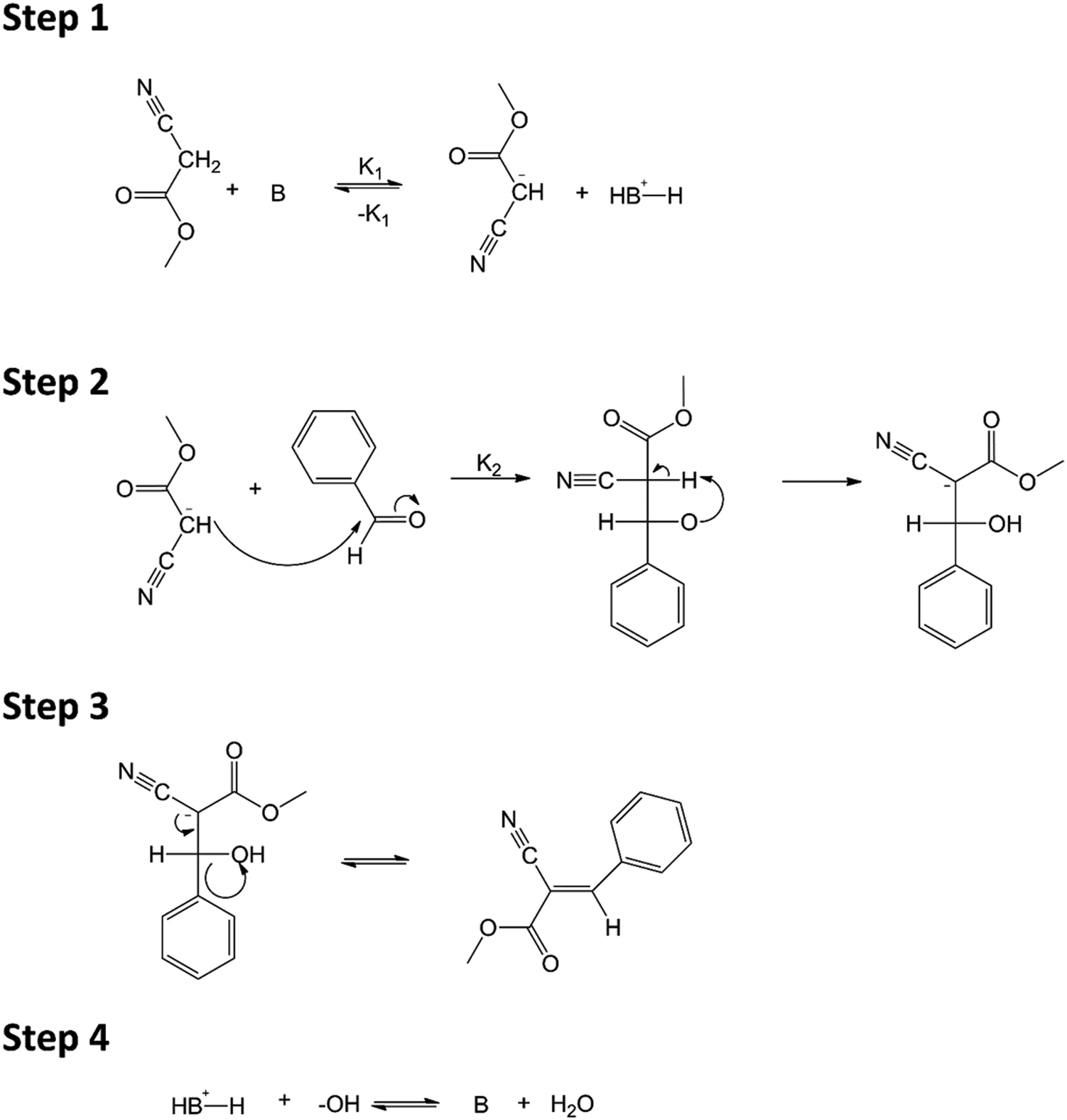
A mechanistic study of the Knoevenagel condensation reaction: new insights into the influence of acid and base properties of mixed metal oxide catalys ... - Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C7CP04743F

Mechanism of the Piperidine-Catalyzed Knoevenagel Condensation Reaction in Methanol: The Role of Iminium and Enolate Ions | The Journal of Physical Chemistry B
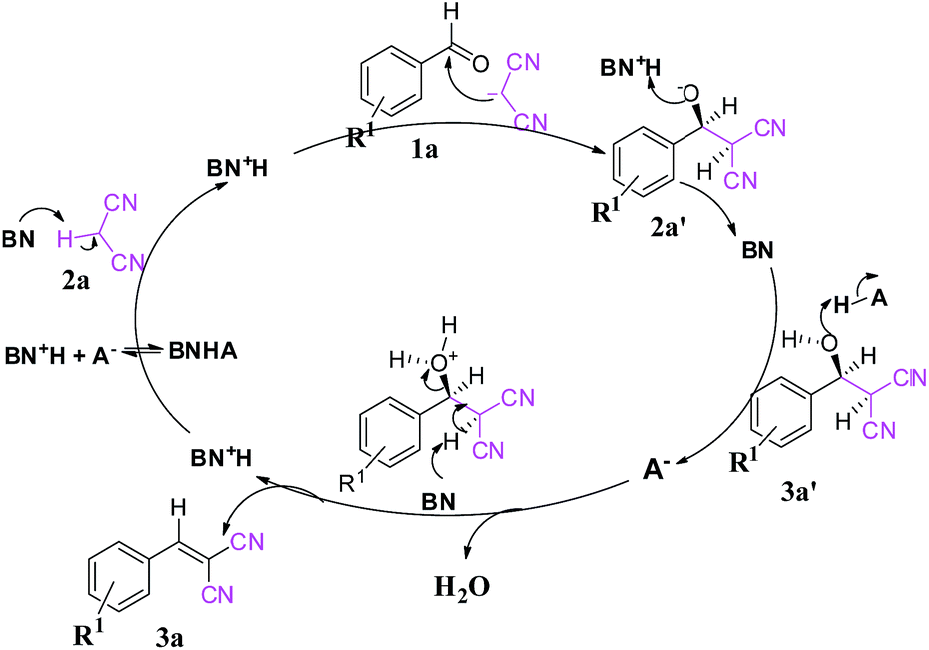
First report of the application of simple molecular complexes as organo-catalysts for Knoevenagel condensation - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C5RA09036A

Mechanism of the Piperidine-Catalyzed Knoevenagel Condensation Reaction in Methanol: The Role of Iminium and Enolate Ions | The Journal of Physical Chemistry B












